detectie carie marginala
Transcript of detectie carie marginala
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
1/10
1
Early Clinic
Re-restoration of Teeth accounts for over 50% of dental work(Elderton et al.1985; Mjor and
Toffenetti 1992)caries rate declining worldwide (Downer,
1984; Rensen et al. 1985).All restorations have built in
obsolescence.
Early Clinic
Reasons for Failure of Restorationsrecurrent caries (>50%) - most common reasongiven by dentists
other technical failures restoration fracture marginal breakdowncusp fracturedefective contour (overhang, wear, open contact)poor appearance
Early Clinic
When to replace existing
restorations?
Early Clinic
Recurrent (Secondary) Decay Definition Microbiology and
Histopathology Location Clinical diagnosis Examples
Early Clinic
Definitions of recurrent caries Spread of caries at the DEJ Failure to remove all diseased tissue Marginal defects of any sort Caries at new site on previously
restored tooth Lesions at the margins of existing
restorationsEarly Clinic
Histology of Secondary Caries Described as having two
partsOuter lesionWall Lesion
Hals E. Andreassen BH. Bie T. Caries Research. 8(4):343-58, 1974.
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
2/10
2
Early Clinic
Secondary Caries Process
Outer lesion - the enamel caries
formed on the surface enamel as a
result of new, primary attack.
Related to plaque accumulation on
the surface similar to primary
caries
Can visually assess wall lesion
Early Clinic
Secondary Caries Process
Wall lesion - which forms as a result
of leakage of bacteria, fluids or
hydrogen ions between restoration
and cavity wall.
This clinically undetectable leakage
around a restoration is referred to as
microleakage
microleakage
Cannot visually assess wall lesion
Early Clinic
Secondary Caries ProcessThe Outer Lesion - Same characteristic
features as early primary caries*Opaque white color early*Progresses through same characteristic histologic stages
incipientcavitated
Early Clinic
Microscopic Features of Incipient Caries Defined Zones
Zone 1 TranslucentZone 2 DarkZone 3 BodyZone 4 Surface
*Surface initially mineralized while
subsurfaces demineralize
*Stages based on pore sizes developing
from demineralization
*Later surface collapses and cavitates12
3
4
Early Clinic
Secondary Caries ProcessPresence of wall lesion questionable
Since caries process follows the
enamel rods
May just be in cases where enamelrods directed to restoration interface
Or when microleakage is primary
cause of secondary decay problem
Early Clinic
Microbiology Most researchers agree that secondary
caries is the same as primary caries
adjacent to a restoration. the pellicle that forms on materials may be
different than the pellicle that forms on
tooth the initial plaque colonization may be
different
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
3/10
3
Early Clinic
Where is recurrent caries most
likely to occur ?
Early Clinic
Location Of Secondary Caries It has been recognized by clinician for
many years (GV Black 1908) and
shown in numerous studies that
secondary caries is more prevalent at
the gingival margins of class II, III, IV
and V restorations than other surfaces.
Early Clinic
Frequency of secondary caries at
cervical and interproximal . 94% of amalgams that fail from caries
fail at these sites. Amalgams rarely
fail at occlusal surface 62% of composites fixed restorations - also would most
likely be proximal areas. Mjor IA. Operative Dentistry. 10(3):88-92, 1985
Early Clinic
Extension for Prevention Recognition of rebeginning or recurrence
of decay at cavity margins (GV Black: A
Work on Operative Dentistry. 1908) Clinical observation led to idea of
extension for prevention (Need to placemargins in areas accessible to inspection and
mechanical oral hygiene measures)
Early Clinic
Location Of Secondary Caries Relationship between proximal cavity
design and recurrent caries. Otto andRule, J Am Dent Assoc 1988;116:867-870
Difficult to determine primary vs secondary
in this particular area.
Early Clinic
Factors that predispose the gingival areas
Clinical Techniques Materials Properties Patient factors
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
4/10
4
Early Clinic
Patient Factors Caries Risk (strep mutan count)
Oral hygieneDietGenetic predispositionFluorides
Early Clinic
Technique Factors Moisture control Access Technique
Condensationbonding
Early Clinic
Materials Properties Different materials have different potential
to seal at restoration marginsAmalgamCompositeGlass ionomers, resin modified GIs
Early Clinic
Materials Properties Amalgam Proper adaptation of amalgam at margins
Minimize voids and irregularities Proximal contours and contacts (overhangs
and open contacts) Some potential caries inhibition (corrosion
products)
Early Clinic
Materials Properties Composite Contraction on polymerization
Volume relatedAll large composite restorations leak
No ability to inhibit caries Seals well on enamel margins but poor on
dentin and cementum margins
Early Clinic
Materials PropertiesGI and RMGI Ability to inhibit recurrent caries (some
evidence but not definitive). Tend to have zero net shrinkage and seal
well.
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
5/10
5
Early Clinic
Methods of Diagnosing Recurrent Caries Visual assessment of color Gap or defect size Hardness Bitewing radiographs
Early Clinic
Appearance of Outer Lesion Range from
white spotbrown spot with or
without softening
of mineralized
tissuefrank cavity
Early Clinic
Color Changes (amalgam) particularly difficult to
interpret adjacent to amalgam
restorations gray or blue discolorations
may indicate either a carious
lesion or corrosion or light
reflecting from the amalgam
itselfEarly Clinic
Color Changes (composite) more easily interpreted. discolorations adjacent to
composite may be a result of discolored
demineralized dentin deep
in the cavity wall or a line of stain at the
junction of the filling and
the tooth.
Early Clinic
Color Changes (composite) The development of stain around a
composite filling may indicate the
onset of early secondary caries. Transillumination is helpful in the
diagnosis of discolored dentin beneath
a tooth-colored restoration.
Early Clinic
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
6/10
6
Early Clinic Early Clinic
Early Clinic Early Clinic
Early Clinic Early Clinic
Secondary caries and Margin defects A ditched amalgam has
long been regarded with
suspicion by clinicians and
are often replaced as a
preventive measure toavoid plaque stagnation
and secondary caries
activity
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
7/10
7
Early Clinic
Marginal Gap or Defect Size No good correlation between gap size
and recurrent decay Larger gaps (>250 m) more likely to
accumulate plaque Plaque accumulations may be decisive
factor
Early Clinic
A catch on a restoration interface
is not synonymous with caries.
Early Clinic
Hardness The clinical parameters that correspond
to heavily infected dentine was
softness to probing, hard and medium-hard areas being
very lightly infected with micro
-organisms. Only frank cavitation was a good
predictor of caries at the DEJ
Early Clinic
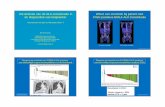
Bitewing Radiographs limited value because of shadowing effect
of restorative materials (amalgam)restorative materials should therefore be same
radiopacity as tooth to maximize detection improve caries diagnosis significantly
compared to other methodsPoor sensitivity 30-50%Good specificity 90%+
Early Clinic
Decay can be more rapid under
composite resin restorations
Early Clinic
Conclusions: (recurrent caries) Initiation and progression similar to
primary caries Microbiology similar to primary caries Secondary caries rarely found inocclusal areas Most often found in gingival areas Margin gaps or ditching not good
indicator of 2 caries
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
8/10
8
Early Clinic
Conclusions: (recurrent caries) Multiple modes of evaluation Frank cavitation, hardness, bitewings are
considered best clinical indicators Color better for composite than amalgam Patient caries risk assessment counts
Early Clinic
Replacing Amalgam Restorations
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Isolation (rubber dam) High-vac suction Copius water spray Remove in chunks if possible
High-speed grinding releases mercuryvapors (concern)
Early Clinic
Mount Extracted Tooth
Early Clinic
Mount Extracted Tooth
Early Clinic
Mount Extracted Tooth
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
9/10
9
Early Clinic
Amalgam removal Use 330 carbide Other special
designs just forrapid removal
34 330
Early Clinic
Amalgam removal Channel throughthe center of the
isthmus frommesial fossa todistal fossa at thedepth of thedentin or base ofpulpal floor
Early Clinic
Amalgam removal Separate box
from isthmus by
extending to
buccal and ling
walls at depth of
pulpal floor or
baseEarly Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Try to remove in
large pieces do not pry hard
enough to breakinstrument-youpay)
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Boxes are
generally locked
in mechanically
due toconvergence of
B-L walls
-
8/3/2019 detectie carie marginala
10/10
10
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Section box
portion in half
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Remove pieces
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Remove pieces
Early Clinic
Amalgam Removal Technique Determine where
or if recurrent
caries is present Base needed? Restore