GUÍA CLÍNICA PARA LA SUPLEMENTACIÓN CON Sci ent i f i c Op i … · 2016. 6. 2. · reconf ir...
Transcript of GUÍA CLÍNICA PARA LA SUPLEMENTACIÓN CON Sci ent i f i c Op i … · 2016. 6. 2. · reconf ir...

GUÍA CLÍNICA PARA LA SUPLEMENTACIÓN CON
PROBIÓTICOS EN FARMACIA COMUNITARIA Fernandez Hospido, N1.;Regal López, Patricia; Cardelle Cobas2, A.2; Cepeda Saez, A.3;Fente Sampayo, C4. 1. Farmaceutica y estudiante Grado Nutricion y Bromatologia.
2. Profesora universitaria. Area Nutricion y Bromatologia. Universidad Santiago de Compostela.
3. Catedrático del Area Nutricion y Bromatologia. Universidad Santiago de Compostela. Farmacéutico Titular en O Burgo, La Coruña.
4. Profesora Titular del Area Nutricion y Bromatologia. Universidad Santiago de Compostela. Farmacéutica Titular en la farmacia La Salud, Lugo.
Palabras clave: Probiotico, Revisiones sistematicas. Guia de practica clinica. Valoracion de tecnologias en salud. Calidad de la evidencia. Fuerza
de recomendacion.
Se ha elaborado una guia clinica que permitira a los farmaceuticos comunitarios seleccionar facilmente el producto con
probioticos adecuado, la dosis y la via de administracion para cada indicacion especifica.
Sólo microorganismos vivos que en estudios controlados en humanos han demostrado conferir beneficios para la salud
EFSA Journal 2013;11(11):3449
Suggested citation: EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards), 2013. Scientific Opinion on the maintenance
of the list of QPS biological agents intentionally added to food and feed (2013 update). EFSA Journal 2013;11(11):3449,
106 pp. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3449
Available online: www.efsa.europa.eu/efsajournal
© European Food Safety Authority, 2013
SCIENTIFIC OPINION
Scientific Opinion on the maintenance of the list of QPS biological agents intentionally added to food and feed (2013 update)1
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ)2, 3
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Parma, Italy
This output, published on 11 December 2015, replaces the previous output published on 25 June 2015.*
ABSTRACT
EFSA is requested to assess the safety of a broad range of biological agents in the context of notifications for
market authorisation as sources of food and feed additives, enzymes and plant protection products. The qualified
presumption of safety (QPS) assessment was developed to provide a harmonised generic pre-assessment to
support safety risk assessments performed by EFSA’s scientific Panels. The safety of unambiguously defined
biological agents (at the highest taxonomic unit appropriate for the purpose for which an application is intended),
and the completeness of the body of knowledge are assessed. Identified safety concerns for a taxonomic unit are,
where possible and reasonable in number, reflected as ‘qualifications’ in connection with a recommendation for
a QPS status. The list of QPS recommended biological agents is reviewed and updated periodically. Therefore,
the only valid list is the one in the most recently published scientific opinion. The 2013 update reviews
previously assessed microorganisms including bacteria, yeasts, filamentous fungi, oomycetes and viruses used
for plant protection purposes. All taxonomic units previously recommended for the QPS list had their status
reconfirmed. The new notifications since the last QPS update were reviewed. Gluconobacter oxydans and
Alphaflexiviridae were assessed for the first time and were recommended for the QPS list. The information of
the previous opinion was updated for the taxonomic units on the QPS list. Qualifications for the taxonomic units
included in the QPS recommended list were reviewed and confirmed. Filamentous fungi and enterococci were
not recommended for the QPS list following updating and reviewing of current scientific knowledge.
© European Food Safety Authority, 2013
KEY WORDS
safety, QPS, bacteria, yeast, fungi, virus
1 On request from EFSA, Question No EFSA-Q-2013-00019, adopted on 24 October 2013. 2 Panel members: Olivier Andreoletti, Dorte Lau Baggesen, Declan Bolton, Patrick Butaye, Paul Cook, Robert Davies,
Pablo S. Fernández Escámez, John Griffin, Tine Hald, Arie Havelaar, Kostas Koutsoumanis, Roland Lindqvist, James
McLauchlin, Truls Nesbakken, Miguel Prieto, Antonia Ricci, Giuseppe Ru, Moez Sanaa, Marion Simmons, John Sofos
and John Threlfall. Correspondence: [email protected] 3 Acknowledgement: The Panel wishes to thank the members of the Working Group on the maintenance of the list of QPS
biological agents intentionally added to food and feed (2013 update): Pier Sandro Cocconcelli, Pablo S. Fernández
Escámez, Florence Richard Forget, Günter Klein, Tine Licht, Miguel Prieto Maradona, Christophe Nguyen-the, Ingvar
Sundh, Ulf Thrane and Just M. Vlak for the preparatory work on this scientific opinion and the hearing expert: Atte von
Wright, and EFSA staff: Renata Leuschner for the support provided to this scientific opinion.
* The 2013 update list of QPS Status recommended biological agents for safety risk assessments carried out by EFSA
Scientific Panels and Units, as shown in Table 1, is undergoing a revision process in accordance with a self-task mandate
of the BIOHAZ Panel. The revisions will be published as an Appendix to a Statement of the BIOHAZ Panel around every
six months, with the first revision in December 2014 and the last revision as an Appendix to a Scientific Opinion of the
BIOHAZ Panel in December 2016. The most up-to-date QPS list will be published on the web as an Appendix to the
corresponding revision and also as a separate file in connection with the respective revision.
Los efectos descritos para un probiótico solo se pueden atribuir a la cepa
o cepa estudiadas y no a la especie o a todo el grupo de bacterias
acidolácticas o de bifidobacterias o de otro tipo de microorganismos.
• Genero y especie con nomenclatura actualmente reconocida.
• Cepa especifica.
• Unidades formadoras de colonia por cada cepa.
• Almacenamiento recomendado.
• Dosis.
• Informacion de empresa comercializadora.
INFORMACIÓN IMPRESCINDIBLE
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN)
RAZONES para recomendar suplementos CON PROBIÓTICOS y no ALIMENTOS con microorganismos beneficiosos (yogur, kefir, etc…)
Diversidad de cepas con indicaciones concretas.
Dosificacion exacta.
Concentracion o elevado numero de unidades formadoras de colonias (UFC) presentes en los probioticos dosificados.
Facilidad de administracion: (sobres unidosis, viales, capsulas, etc.)
Facilidad de conservacion.
Larga vida media mucho mayor que los alimentos fermentados
Posibilidad de incorporar otros componentes al probiotico dosificado que lo complementen (prebioticos, micronutrientes como vitaminas y minerales…)
Intolerancia a la lactosa
Usuarios que rechazan la textura o el sabor acido de algunos preparados lacteos con presencia de probioticos como yogures o leches fermentadas.
Enfermedad Enfermedad DAA Prevención de la diarrea asociada a
antibióticos.
CU Colitis ulcerosa
E Estreñimiento SII Síndrome de intestino irritable
DCD Prevención de la diarrea por Clostridium
difficile
EN Enteritis necrotizante en recién
nacido
EII-P Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal/Pouchitis IN Prevención de las infecciones
nosocomiales
EI/DA Eczema infantil/Dermatitis atópica PD Enfermedad periodontal
MA Malestar abdominal/cólico DV Diarrea del viajero
HP Helicobacter pylori, tratamiento DI Diarrea infecciosa
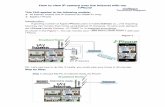
GUIA PARA PEDIATRÍA GUIA PARA ADULTOS
GUIA PARA MUJER
INDICACIÓN POSOLOGÍA Mastitis aguda 1 cáps/cada 8h hasta remisión
(1) Mastitis subaguda 1 cáps/cada 12h hasta remisión
(1) Prevención 1 cáps/24h durante toda la
lactancia
(2) Bienestar íntimo 1 cáps/24h durante 20 días
(2) Fase aguda 2 cáps/24h durante 10 días,
después 1 cáps/24 h 2-3meses
(3) Fase aguda 1 cáps/24 h 6 días
(3) Post-tratamiento 1 cáps/24 h 6 días, después de
cada ciclo
Bibliografía a su disposición y correspondencia: [email protected]
UFC: Unidades formadoras de colonia B: 10 9; M: 106
*: Necesita refrigeración L: lactobacillus B: Bifidubacterium