Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
-
Upload
emman-aguilar -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
1/31
Gastrointestinal agents
Ana Marie L. Rubenicia, RPh
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
2/31
Gastrointestinal Agents
Inorganic agents used to treat gastrointestinal
disorders includes:
1. Products for altering gastric pH
2. Protectives for intestinal inflammation
3. Adsorbents for intestinal toxins
4. Cathartics or laxatives for constipation
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
3/31
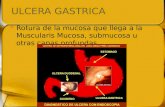
Antacids
Indications: to neutralize excesshydrochloric acid which maybecausing pain or ulceration.
The stomach pH can 1 when emptyor 7 when food is present.
Hyperacidity leads to:
Gastritis general inflammation ofthe gastric mucosa.
Peptic ulcer a specifiedcircumscribed erosion. Can belocated in the lower end of theesophagus(esophageal ulcer)
Esophageal ulcer occurs whenesophageal sphincter is defectivein w/c pateint freuentlyexperience heartburn.
Gastric ulcer located in thestomach
Duodenal ulcer located in theduodenum.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
4/31
Antacids
Depending on the severity
and location of an ulcer
treatment wil range for
diet and antacid and/oranticholinergic therapy
to complete bed rest
and possible surgery.
Frequently , removal of an
emotional stress
situation in indicated.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
5/31
Antacids
Antacids are alkaline
bases used to neutralize
the excess gastric HCl
associated with gastritisand peptic ulcers.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
6/31
Antacids
While no antacid is ideal , there have been certain criteriathat have been developed. These are:
1. The antacid should not be adsorbable or cause systemicalkalosis.
2. The antacid should not be a laxative or causeconstipation.
3. The antacid should exert the effect rapidly and over along period of time.
4. The reaction of the antacid with gastric HCl should not
cause a large evolution of gas.5. The antacid should buffer in the pH 4-6 range.
6. The antacid should probably inhibit pepsin.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
7/31
ANTACIDS
SODIUM BICARBONATE
- highly water soluble
antacid with a rapid
onset of action butrelatively short
duration.
-it can cause a sharp
increase in gastric pH
up to or above pH 7.
-can cause belching and
flatulence due to the
evolution of carbon
dioxide in the presenceof acids.
- found in many
effervescent antacid
preparations.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
8/31
ANTACIDSALUMINUM HYDROXIDE USP 26
The USP 26 recognizes 2 physicalforms:
1. Aluminum Hydroxide GelUSP 26
2. Dried Aluminum Hydroxide
Gel USP 26These aluminum hydroxide gelsare ideal buffers in the Ph 3-5 region due to theiramphoteric characters.
The essential characteristics of
these gels is the fine colloidalparticles that would exhibit alarge surface area and thusgreat adsorptive powers uponwhich its therapeutic valuesdepends.
A problem with these gels isthat of a loss of antacidproperties upon aging.
Due to the product watersoluble AlCl3 of the reaction
with HCl, Al(OH)3 gel causesconstipation and occasionallynausea and vomiting.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
9/31
ANTACIDSALUMINUM HYDROXIDE
USP 26
Uses:
1. Gastric antacid and isnow widely employed in
the treatment ofhyperchlorhydria andpeptic ulcer.
2. It is also indicated forthe treatment oftoxemia due to itscapability of adsorbing
HCl, toxins, gases andbacteria. This is theadvantage of the gelapparent adsorbspepsin.
Caution: can also interferewith adsorption ofother drugs.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
10/31
ANTACIDS
CALCIUMCONTAINING ANTACIDS
This group of antacids differ from the aluminumantacids in that in their action is dependentupon their basic properties and not on anamphoteric effect.
In vitro and in vivo studies show that the calciumantacids raise the stomach pH to nearly 7.
The calcium antacids tend to be constpating andare usually found in combination with
magnesium antacids.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
11/31
CALCIUMCONTAINING ANTACIDS
CALCIUM CARBONATE USP26
Synonyms: Precipitated ChalkProperties: Practically
insoluble in water butsolubility is increased byammonium salts or carbon
dioxide. It is insoluble inalcohol and dissolves witheffervescence in dilutedacetic acid , dil HCl and dilnitric acid.
Uses: because of its fast
action calcium carbonate isone of the most popularantacids.
Its action is limited by theamount of salt that will go
into the solution. Thus, asgastric HCl consumessolubilized CaCO3, moregoes into the solution.
Most CaCO3 preparations will
be found in combination witmagnesium antacidsbecause of calciumsconstipative effects.
USP 26 recognizes Calcium
carbonate lozenges and oralsuspension.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
12/31
CALCIUMCONTAINING ANTACIDS
TRIBASIC CALCIUM PHOSPHATE NF21[Ca3(PO4)2]
Synonyms: Precipitated CalciumPhosphate, Tertiary CalciumPhosphate, Calcium Phosphate
Properties: Insoluble in water andalcohol but dissolves readily in dilHCl and HNO3.
Uses:
As an antacid in the treatment ofhyperacidity by diminishing thehydrogen ion concentration ofthe gastric HCl by the formationof primary and secondary
phosphates.It has the advantage over NaHCO3 in
that there are no gas produced.
It is also used as source of calciumfor the system but due to itsinsolubility , very little Ca is
absorbed and is therefore notavailable in acute calciumdeficiemcy.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
13/31
ANTACIDS
MAGNESIUM CONTAINING ANTACIDS-there are a large number of official antacids containingmagnesium, with the exception of magnesiumtrisilicate, they all function in the same manner.
-they are poorly soluble salts w/c only go into soln as acid
consumes the small amount of anion already insolution. Thus, it is the anion rather than themagnesium cation that confers to its antacid properties.
The magnesium cation causes this group of antacids to belaxatives. For this reason, they are susually found in
combination with Al and Ca antacids in an attempt toequalize the constipative and laxative actions
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
14/31
MAGNESIUM CONTAINING ANTACIDS
MAGNESIUM CARBONATE USP 26[Mg( CO3 )4.Mg(OH)2.5H2O]
Synonyms: Carbonate of Magnesia;Magnesium Carbonate; HeavyMagnesium Carbonate
Properties: Insoluble in alc butdissolves with effervescence in dilacids.
Uses: The antacid properties are dueto the hydroxide and carbonateanions reacting with the gastricHCl.
Due to its very limited solubility,MgCO3 dissolves only ascarbonate and hydroxide arebeing consumed.
MAGNESIUM HYDROXIDE USP 26[Mg ( OH )2]
Properties: Practically insolublein water and alcohol butdissolves in acids.
Uses: Due to its basic character,it is an efficient antacid. Inhigh doses, it used as alaxative. This due to theformation of magnesium
chloride in the stomach w/cexerts a salt action in theintestinal tract causing a mildlaxative action.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
15/31
MAGNESIUM CONTAINING ANTACIDS
MILK OF MAGNESIA
A suspension of magnesiumhydroxide containing nlt 7%and nmt 8.5% Mg(OH)2.
To minimize the interaction ofglass containers andMg(OH)2, small amounts ofcitric acid maybe added.
Suitable flavoring agentsmay also be added.
Uses: very popular antacid andlaxative.
MAGNESIUM PHOSPHATE [Mg3(PO4)2. 5H2O
Synonym: Tertiary Magnesium
Phosphate
Properties: Readily soluble indiluted mineral acids but
almost insoluble in water.
Use: Antacid
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
16/31
MAGNESIUM CONTAINING ANTACIDS
MAGNESIUM OXIDE USP 26(MgO)
Synonyms: Magnesia
Properties:The USP recognizes 2
varieties of medical MgO(differ indensity):
1. Light Magnesium Oxide 5grams occupy a volume ofapproximately 40 to 50 mL andhydrolyzes to Mg(OH)2 moreeasily than the heavy oxide.
2. Heavy Magnesium Oxide 5grams occupy a volume of 10 to20ml.
They are similar in composition andpurity. Upon exposure to air,they absorb carbon dioxide andmoisture.
Uses: Magnesia is employed as
laxative, diuretic and antacid. I
It also given as arsenic
antidote.
In order to prevent the formation
of a gelatinous mass, it should
be administered in about 29
times its weight of water.
The magnesia should be added towater and not the reverse in
order to avoid the formation
of hard lump
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
17/31
MAGNESIUM CONTAINING ANTACIDS
MAGNESIUM TRISILICATE USP26(2MgO.3SiO2.xH2O)
Composition: Defined as acompound of magnesiumoxide and silicon dioxide
containing varying portions ofwater. It contain nlt 20%magnesium oxide and nmt45% of silicon dioxide.
Properties: It is assayed in termsof silicon dioxide and MgO and
must have definite SiO2/MgOratio. As the amount of SiO2increases with respect to MgO,there is lost in antacidproperties.
Use: gastric antacid especiallyvaluable in peptic ulcer.
2MgO.3SiO2.xH2O + 4H+
3SiO2.xH2O+2Mg+2H2O
The colloidal silicic acid orhydrous silica which is formedin the reaction has adsorptive
powers and could protect theulcer from further acid andpeptic attack and possibleadsorbs the pepsin.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
18/31
COMBINATION ANTACID
PREPARATION
Mixtures of antacids are made to balance the constipative effect ofcalcium and aluminum with laxative effect of magnesium. Also, amixture of an antacid with rapid onset of action and one withsupposedly longer duration of action.
a.) Aluminum Hydroxide Gel Magnesium Hydroxide
Combination: Aludrox, Wingel, Maalox, and Cremalib.) Aluminum Hydroxide Gel Magnesium Trisilicate
Combination: Gelusil, Tricreamalate, Triosgel
c.) Magaldrate chemical combination of Al(OH)3 and Mg(OH)2(Riopan)
d.) Simethicone(defoaming agent) containing antacids: Di-Gel,Mylanta. Prevent being gassy.
e) Alginic acid NaHCO3 containing antacids: Gaviscon, Foamtab. Thisformulation attemp to provide symptomatic relief of refluxesophagitis.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
19/31
PROTECTIVES AND ADSORBENTS
Ana Marie L. Rubenicia, RPh
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
20/31
PROTECTIVES AND ADSORBENTS
This group of gastrointestinal agents is
commonly used for the treatment of mild
diarrhea.
Most products for the treatment of diarrhea will
consist of an
1. adsorptive-protective
2. antidiarrheal agent and possibly an
3. antibacterial agent.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
21/31
BISMUTH-CONTAINING PRODUCTS
The use of bismuth salts as antidiarrheal agentseems to be supported chiefly by tradition.
They are considered as water insoluble but a
small amount go into solution. The solublebismuth cation supposedly exerts a mildastringent and antiseptic action.
Intestinal hydrogen sulfide acts upon the
bismuth salts to form bismuth sulfide, hence, theblack stool resulting from the oral administrationof bismuth-containing preparations.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
22/31
BISMUTH-CONTAINING PRODUCTS
BISMUTH SUBNITRATE USP 26
[Bi (OH)2(NO3)4.BiO(O H)]
Synonyms: Basic Bismuth Nitrate;
White Bismuth
Properties: Bismuth Subnitrate
occurs as white, slightly
hygroscopic powder which
gives an acid reaction using
blue litmus paper. It is
practically insoluble in water
and alcohol but dissolves in
HCl . It is assayed in terms of
bismuth trioxide (Bi2O3).
Bismuth subnitrate is incompatiblewith tragacanth, in whichtragacanth precipitates as a hardmass in the presence of the salt.The difficulty maybe overcome bthe addition of sodium
biphosphate or trisodiumphosphate.
Uses: it is used as an effective non-irritant intestinal antiseptic.Bismuth salts lessens gastricsecretion and reduce acidity,
hence it is employed in treatinggastric ulcers and inflammations.Bismuth Subnitrate is a commonremedy against diarrhea.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
23/31
BISMUTH-CONTAINING PRODUCTS
BISMUTH SUBCARBONATE USP26 [BiO2(CO3)2. H2O]
Synonym: Basic BismuthCarbonate
Properties: It is a white or pale
yellowish white,odorless,tasteless powder which isstable in air but is slowlyaffected by light. It ispractically insoluble in waterbut dissolves in HCL with
effervescence. BismuthSubcarbonate is assayed interms of its bismuth trioxidecontent.
Uses:
It is used for its protective andantacid effect ininflammations of the stomachand bowels.
It is also given in large doses (60grams) for rendering thealimentary canal opaque to x-ray.
It is used as an astringent andadsorbent and in the
treatment of diarrhea anddysentery.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
24/31
BISMUTH-CONTAINING PRODUCTS
MILK OF BISMUTH USP 26
Synonyms: Bismuth Magma,Bismuth Cream
Uses: Astringent and antacid
Composition: Milk of Bismuth
contains bismuth hydroxide andbismuth subcarbonate insuspension in water.
It is made by concerting bismuthsubnitrate to bismuth nitrate bythe addition of nitric acid. Then,by the treatment with
ammonium carbonate andammonia solution, bismuthnitrate is converted to bismuthhydroxide and subcarbonate.
ACTIVATED CHARCOL USP 26
has been as an adsorbent in thetrEatment of diarrhea. I
t is now recommended as anantidote in certain types ofpoisoning.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
25/31
KAOLIN USP XX 26
Synonyms: Porcelain Clay; ChinaClay; Bolus Alba
Properties A soft, yellowishwhite or whitish powder or in
lumps, insoluble in water andin cold dilute acids and insolutions of alkali hydroxides.It has an earthly and clay-liketaste. When moistened withwater, it assumes a darker
color and develops a markedclay-like color.
Uses: It is usually foundtogether with the vegetablecarbonate, pectin(Kaopectate, Kao-Con) andemployed as a protective sndadsorbent (Kaopectate, Kao-Con) and employed as aprotective and adborbent indiarrheal disorders.
Kaolin-containing products havebeen reported to interfere
materially with the intestinalabsorption of lincomycin.
SALINE CATHARTICS
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
26/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
Saline cathartics (purgatives) are agents that quicken and increaseevacuation from bowels. Laxatives are mild cathartics . Mostproducts can be purchased without prescription hence this grouphas been widely used, abused and often overprompted by themanufacturers.
The 1972 AMA Drug Evaluation states the criteria whencathattics are properly used:
1. To ease defecation in patients with pAinful hemorrhoids orother rectal disorders.
2. To avoid potentially hazardous rises in blood pressure during
defecation in patients with hypertension, cerebral arterialdiseases.
3. To relieve acute constipation,
4. To remove solid material from the intestinal tract prior tocertain roentgenographic studies.
SALINE CATHARTICS
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
27/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
4 Types of Laxatives:1. Stimulant Laxatives act by local irritation on the intestinal tract, whichincreases peristaltic activity.
2. Bulk-forming Laxatives are made from cellulose and other non-digestiblepolysaccharides which swell when wet and with the increased bulk stimulatesperistalsis.
3. Emollient Laxatives act neither as lubricants facilitating the passage ofcompacted fecal material or as stool softeners. Example is Mineral Oil.
4. Saline Cathartics act by increasing the osmotic load of the gastrointestinaltract. They are salts of poorly absorbable anions and sometimes cations. Thebody relieves the hypertonicuty of the gut by secreting additional fluids into theintestinal tract. The resolution increased bulk stimulates peristalsis.
Poorly absorbed anions that are used as saline cathartics are biphosphate,phosphate , sulfate and tartrate. Soluble magnesium salts are cathartic due tothe poorly absorbed magnesium ion. The saline cathartics are water solubleand are taken with large amounts of water. This prevents excessive loss of bodyfluids and reduces nausea and vomiting if a too hypertonic solution shouldreach the stomach.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
28/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
MONOBASiC SODIUM PHOSPHATE
USP 26 [NaH2PO4.H2O]Synonyms: Sodium Dihydrogn
Phosphate; Sodium AcidPhosphate; Primary SodiumPhosphate; Sodium Buphosphate
Properties: A colorless crystals or as
a white crystalline powder. It isodorless and is slightlydeliquescent. Its solution areacid to litmus and effervescewith sodium carbonate. These 3acidic properties are due to theacid dihydrogen phosphate
anion. The USP 26 recognizessalt in the anhydrous form andwith one or two moles of waterof hydration.
Uses: Official category is as urinaryacidifier.
It is also used as a cathartic. Thissalt is used to render the urineacidic in case of cystitis withhexamethylenetetramine
(Methenamine), as thissubstance decomposes intoformaldehyde only in thepresence of acids.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
29/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
DIBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE
USP 26[Na2HPO4.7H2O]
Synonyms: Dibasic SodiumPhosphate; DisodiumHydrogen Phosphate;Secondary Sodium Phosphate
Properties: Sodium Phosphateoccurs as a colorless or whitegranular salt which effervescesin warm dry air. Its solutions
are alkaline to litmus andphenolphthalein with a pH of9.5. It is freey soluble to waterand very soluble in alcohol. Itis also official with one, two,seven or twelve moles water
of hydration.
Uses: Because of the poorintestinal permeability of themonohydrogen phosphate ion,this product is widely used asa saline cathartic.
Caution: This Sodium Phosphate(Dibasic) should never beconfused with the commercialtribasic sodium phosphatewhich is very alkaline andcaustic and should be used for
intestinal purposes.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
30/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
POTASSIUM SODIUM TARTRATE USP
26 KNaC4H4O6.4H2OSynonyms: Rochelle Salt; Seignette
Salt
Properties: Occurs as colorlesscrystals or as a white crystalline
powder having a cooling salinetaste. Because of it efflorescesslightly in warm, dry air , thecrystals are often coated with awhite powder. It is freely solublein water and practically insolublein alcohol.
Uses: The main use of Rochelle Saltin therapeutics is as cathartic, itsactivity ranging from mildlaxative to the more potenthydragogue depending upon thedose administered.
It is a pharmaceutical necessity and
an ingredient of Seidlitz powderwhich is in the form in which
potassium sodium tartrate is
administered as cathartic. It is
an effervescent preparation and
is a palatable product.Rochelles Salt is one of the
components of the useful
reagent, Fehlings Solution,
officially called Alkaline Cupric
Tartrate. This is an example ofthe chelate complexation
wherein the concentration of the
cupric is very little and is not
precipitated by the NaOH
present in the reagent.
-
7/27/2019 Gastrointestinal agents.pptx
31/31
SALINE CATHARTICS
MAGNESIUM SULFATE USP 26[MgSO4.7H2O]
Synonyms: Epsom Salt; Bitter Salt
Uses: An active cathartic operating
with but little pain or nausea and
producing watery stools.
Parenterally, it is used as an
anticonvulsant, It I also used locally
in saturated solution for its
anecthetic effect in sprains and
bruises and appears to be possessedodFsome sort of antiphlogistic
action.
MAGNESIUM CITRATE USP 26
Synonyms: Citrate of Magnesia;Purgative Lemonade
NON OFFICIAL SALINE CATHARTICS
1. SODIUM SULFATEGlaubers Salt
2. POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE Dibasic
Potassium Phosphate, Dipotassium
Hyrogen Phosphate, DKP
3 POTASSIUM BITARTRATE Cream of
Tartar, Potassium Acid Tartrate,
Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate
4. CALOMEL Mercurous Chloride, Mild
Mercury Chloride