Gastric Ulcer
-
Upload
fatima-awadh -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.570 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Gastric Ulcer

FATIMA AL-AWADH
Gastric Ulcer

• THE STOMACH IS THE FIRST INTRA-ABDOMINAL PART OF
THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
• IT IS A MUSCULAR, HIGHLY VASCULAR BAG-SHAPED
ORGAN. • THE STOMACH LIES IN THE
LEFT UPPER QUADRANT OF THE ABDOMEN.
Introduction

Objectives
Mention the anatomy and histology of the stomach.
Define and display the morphology of gastric ulcer.
Mention the risk factors & causes of gastric ulcer.
Explain the pathophysiology of gastric ulcer.

Pylorus Pyloric canal
Anatomy of the stomach
FundusCardi
a
BodyPyloricantrum
ESOPHAGUS
Duodenum

Histology of the stomach
Gastric pits
Gastric glands
Muscularis mucosa
Blood vesselsOblique muscle
layerCircular muscle layerLongitudinal muscle layerConnective tissue layerVisceral
peritunium
Mucosa
Sub-mucosa
Muscularis
Serosa

Ulcers
An ulcer is a medical condition caused by a break in a bodily membrane.
Common forms of ulcers include:
Skin ulcer
Genital ulcer
Mouth ulcer
Peptic ulcer
Venous ulcer
Ulcerative
colitis

Gastric ulcer
A break in the normal tissue that lines the stomach.
A type of peptic ulcers.

Morphology
Gastric peptic ulcers are
predominantly located near the interface of the
body and antrum.

Statistics per 100,000 inhabitant
no data less than 20 20-80 80-140 140-200 more than 200

Risk Factors
Non-steroidal anti-inflammat-ory drugs
Helicobacter (H) Pylori infection
Smoking Increasing age
Alcohol abuse

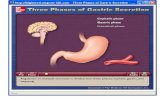
Pathophysiology
1 .Aggressive factor
H. PyloriNSAIDs; Aspirin Corticosteroi
ds
Alcohol abuse
Cigarette smoking

Pathophysiology
2 .Increased gastric acidity
ClH K C
l
NaC
l
ClH
ClH K C
l
KCl
NaC
l
Na C
l

The increasing acidity
Increase in the process pepsinogen→ pepsin rate
Activation

Pathophysiology
3 .Impaired defensesDecrea
se in
Epithelial
transport
Mucosa secretio
n
HCO3¯ secreti
on
Blood flow

Pathophysiology
4 .Gastric ulcerSome cells die
due to ↑ digestive enzymes and
↓ defense in the stomach.

Pathophysiology
4. Gastric ulcer

References
Clinically Ordinated Anatomy, 6th ed. Pg233,Figure2.37.B.
Anatomy of the stomach
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/media/68634/Structures-of-the-human-stomach-The-stomach-has-three-layers
Histology of the stomach
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ulcer Definition and types of ulcer
http://ak47boyz90.wordpress.com/2010/09/02/l5-patho-peptic-ulcer-disease/
Morphology
\http://www.umm.edu/patiented/articles/who_gets_peptic_ulcers_000019_5.htm
Risk factors
\http://www.histopathology-india.net/PepUlc.htm
Pathophysiology