EDU 3103 w10
-
Upload
thecla-thekev -
Category
Documents
-
view
237 -
download
0
Transcript of EDU 3103 w10
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
1/42
Edu 3103 Learning and
the LearnerWeek 10
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
2/42
1. Definition, Types and Principles of teachingapproaches
- Inductive, Deductive, Integrative, Eclectic- Thematic
2. Definition, Types & Principles of teachingstrategies
- Teacher-centred
- Pupil - centred
- Resource-based
- Task/Activity-based
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
3/42
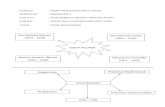
Teaching Frame
There are 4 levelsnamely models,approaches, strategies,
methods andtechniques
Methods & techniques
strategies
approach
models
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
4/42
Teaching models
Frames or guides that can be made as apoint to explain the teaching and learningprocesses that are carried in a classroom
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
5/42
Teaching Approach
A set of assumptions based on teachingmodels, theories or principles which are tobe implemented for a class lesson with the
aim to achieve the predetermined objectives
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
6/42
Teaching strategy
Wisdom to choose a teaching approach aswell as the competency in organizingteaching methods and techniques for the
implementation of a lesson based on a pre-determined teaching and learning objectives
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
7/42
Teaching methods
An organization and application of teachingtechnique, teaching materials, teaching aidsand supplementary materials by the teacher
with the aim of achieving the teaching andlearning objective
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
8/42
Inductive Approach
Normally involves the activity of collecting, analyzing andinterpreting information grouped together and then arrivesat a certain concept or generalization
A teacher usually begins the lesson by introducing a few
specific examples that contain common attributes orcharacteristics.
Based on the examples given, students are guided tostudy, analyze, interpret and to abstract the commoncharacteristics contained in each of the specific examplesand then derive a certain concept or generalization
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
9/42
B. Seaton (1982): A mental process wherebya student observes certain events to comeup with a generalization.
Specific
examples
To observe,study, ascertain,
interpret
Derivegeneralization,
concept,principles, law
Gold fish,tadpole,shark
Use gills
to breathe Fish and othercreatures live in
water use Gills to breathe
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
10/42
Principles of Inductive Teaching
Examples must be relevant and suitable
Teacher guides students to drawconclusion.
Teacher gives opportunity to students toobserve and analyze the examples so thatmaking generalization takes place
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
11/42
Principles of Inductive Teaching
Teacher plans teaching activities thatincorporate specific examples to makegeneralization or conclusion.
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
12/42
Application: In Science (Magnet)
Students are given a heap of materials
(paper clips, eraser, plastic button, nails,money, pencil, thumb tacks, plastic ruler andmetal ruler)
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
13/42
Students are given magnet and do experimentwhich material will be attracted to the magnet.
After the activity, students and teacher discuss on
characteristics of the materials that are attractedto the magnet. Finally, students are asked to draw conclusion in
sentences about their experiment
Student will draw conclusion that magnet willattract materials made from metalTeacher finishes the lesson by emphasizing the
generalization made in a graphic or visualpresentation
The graphics and conclusion will help student tofocus on the lesson
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
14/42
Deductive Approach
Formation of concept using deductive approachbegins with the concept that are already acquiredto produce a new concept by means of logical
reasoningThis approach is also used to obtain new formula,
principle, conclusion or generalization based onformulae, principles, laws, theorems or rules whichhave been learned
In teaching, the DA begins using one or severalformulae, principles, laws or theorems tocomprehend, interpret or solve certain specific butrelated problems
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
15/42
Deductive method is a complex teachingmethod because students need to have a
profound understanding and sufficientknowledge as well as the ability to selectthe relevant formulae, principles, laws,
theorems or rules which have beenlearned so as to apply them on thespecific examples.
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
16/42
Formulae,principles
or ruleswhich have
beenlearned
Deductivemethod
Application of formulae,principles, theorems
or rules
To derive newformulae, principles
, theorems or rules
Area ofrectangle= l x b
Area ofhalf of
rectangle = l x b2
Area oftriangle
=1/2 x l x b
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
17/42
Using the example of magnet, the teacher willtell that magnet can attract certain objects i.e.
metalTeacher will explain the concept of attraction
and pose the question : Will magnet attractpencil? Discussion will be done with some
experiments whereby teacher gives students amagnet and ask them whether objects in theclassroom are attracted to the magnet
At the end of the discussion, teacher and
students draw conclusion that magnet onlyattracts metal object based on the experimentand examples in the classroom
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
18/42
Eclectic Approach
This approach is basically an alternativecombination of inductive and deductiveapproaches used for formation of concepts,
principles, theorems, laws, formulas ortheories
Suitable for the classroom with students ofmixed abilities where at times, inductiveapproach works and deductive at othertimes
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
19/42
E.g. Teacher starts with examples
followed by generalization. Teacher canend the lesson by giving examples toconsolidate laws and generalization
(Inductive). Or teacher can start withrules or generalization followed byexamples and end by explaining aboutlaws again (deductive)
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
20/42
This approach is commonly used inteaching Mathematics and Science where
both approaches are used alternatively toform concepts, principles, theorems, lawsor formulae which are to be used for
application in problem-solvings
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
21/42
Mathematics
Inductive deductive
2x3=6
3x2=6 application
4x5=20 axb=bxa10x5=5x10
5x4=20
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
22/42
Science
Inductive Deductive
Fish ApplicationCat
Bird Animals
Dog with backbone(vertebrate) duck
hen
goatcow
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
23/42
Integrated Learning
Phase 1: Describing
Phase 2: Comparing
Phase 3: ExplainingPhase 4: Hypothesis
Phase 5: Making generalization
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
24/42
Integration means fusion or combinationof skills or contents from one or more
than one subjects into another subjectIn the Primary School Integrated
Curriculum (KBSR), teaching is done inintegration of several skills
Example: Students are taught throughthe integration of 4 skills i.e. reading,writing, speaking and listening; content
knowledge from certain topic can beintegrated into another subject duringthe process of learning
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
25/42
Reading skillRead &
understanda Mathematical
problems
Writing skillWrite down
thesolution steps
Counting skillCalculatethe answer
Verbal skill
Explainverbally
theanswer obtained
Language skills Mathematic skills
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
26/42
Thematic approach
Teaching using theme
Theme is broken into smaller components
Enable students to analyze, make generalization
and apply knowledge Enable students to combine many facts under one
theme
Enable students to have different experience fromdifferent situation
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
27/42
Purpose of thematic approach:
1. Strategy is students centered
2. Based on theme3. Students active involvement in thematic
teaching
4. Cohesiveness
5. Skill activities are combined to increasestudents potential
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
28/42
Principles of thematic approach
1. Theme chosen must be suitable to the
interest , ability and experience of students2. Theme should be related to daily life of
students
3. Theme should have wide scope and coversvarious fields
4. The sequence of theme is in order/systematic
5. Activities based on theme covers different
fields in curriculum
6. Development of theme should ignite ideas
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
29/42
Steps in implementation of Thematicapproach
1. Choose 1 theme
2. Build plan network
3. Choose materials
4. Plan activities
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
30/42
Teaching & Learning Strategies
Teachers centered
Students centered
Resource centeredTasks@ activates centered
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
31/42
Teachers Centered Strategy
Teacher controls all the teaching and learningactivities in the classroom
Teaching is based on expository teaching model
Methods of teaching: whole-class teaching,demonstration, lecture, story telling
Teacher talks a lot; students sit quietly and listen
a lot
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
32/42
Characteristics of Teacher-Centered Strategy:
1. Teacher plays primary and active role;students play passive role as listeners oraudience
2. One-way interaction and communicationbetween teacher and students
3. Autocratic teaching style4. Teaching strategies planned according to
teaching objectives only
5. Emphasize only on the learning of subject
matter and skills rather than to foster noblevalues or socio-emotional development
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
33/42
6. Emphasize on the pupils achievement intests and examination
7. Passive interaction with very limitedsocial interaction and communicationamong pupils
8. Emphasize on the whole classorganization, adopt whole class teachingmethod and ignore individual differences
9 Pupils become less creative and are notencouraged to take their own initiativeto learn
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
34/42
Pupil-Centred Strategy
Students play a primary role in the learningprocess
Pupils are encouraged to take active part inlearning; teacher plays a facilitating role and
guide the pupils to learn either individually orin small group
Most of the learning time will be allotted forpupils activities
Methods of teaching are individual learning,group activity, inquirydiscovery, discussion,brainstorming, simulation, role play andproblem solving
h f l d
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
35/42
Characteristics of Pupil-Centered Strategy1. Students primary role in the learning process;
teacher as facilitator guiding students to
learn either individually or in small group2. Interaction and communication processbetween teacher and students is two-way i.e.teacher applies facilitating techniques toguide pupils to response
3. Teacher practices democratic reaching styleand pupils are encouraged to air theiropinion thorough discussion
4. Emphasize on the achievement on the
learning objectives of the pupils5. Emphasize on the overall development of
students potentials
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
36/42
6. Emphasize on the formative test to ascertainpupils weaknesses in learning
7. Interaction process among students are manyto foster social skills and noble values
8. It places importance in carrying out students
activities in small groups9. Emphasizes on the organization of group
activities according to individual difference
10. People tend to be more innovative and
creative and take their own initiative to learn
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
37/42
Material-Centered Strategy
Emphasize the use of teaching and learningmaterials during the teaching and learning process
Teaching materials used as teaching aids are
chart, maps, specimens, model, film slides, radio,tape recorder, projector, television, video andcomputers.
Teacher are able to present the lesson effectivelyand in an intersecting manner
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
38/42
Learning materials are material used bystudents such as text book, work sheets,printed materials, modules, laboratory
apparatus and computer
Teaching methods: audio-visual method usingtape recorder, projector, television and video,
programme instructional teaching usingcomputer and software and modular teachingusing printed materials; experiential methodsusing laboratory apparatus; inquiry-discovery
using science apparatus, demonstration usingcharts, diagram
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
39/42
Applications of materials-centered strategyinvolve teacher-centered strategy. E.g. a
teacher may use teaching aids to demonstrateor explain a certain teaching activity
Some of the applications of material-centeredstrategy involve students-centered strategy.
E.g. when using teaching methods such asinquiry-discovery, problem solving or projectmethods, pupils need to use learning materialsto perform, investigate and study to carry outtheir learning activities or assignments
Characteristics of Material-Centered
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
40/42
Characteristics of Material CenteredStrategy
1. Teacher and students need teaching
and learning materials to optimizeteaching and learning inside andoutside the classroom
2. Provide opportunity for interaction andcommunication among the teacher,students and teaching aids
3. The skills of using teaching and
learning aids play the primary role toachieve the pre-determined objectives
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
41/42
5. Emphasizes on the overall development of thepupils potentials, especially development ofcognitive, physical, emotional and socialaspects
6. With teaching aids, teachers will be able topresent the lesson clearly, accurately and in aninteresting manner
7. With learning aids, pupils will be able todevelop their manipulative skills, and fosterwith positive attitude in group activities
8. This strategy provides opportunity for
meaningful teaching and learning experiences,whereby abstract knowledge and skills areacquired through concrete practical expereices
-
8/3/2019 EDU 3103 w10
42/42
Task-Based Strategy
Based on learning activities that are planned bythe teacher for pupils, to carry a certain task. Asthese learning activities required teaching andlearning materials, it is closely related with
material-centered strategy as well as pupil-centered strategyTeaching methods and activities under this task-
based strategy are role play, drama, project suchas model making, discussion such as debate and
brainstorming, and other assignment activities