DW Lecture 01
-
Upload
engineerkhaula7035 -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of DW Lecture 01
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
1/21
Lecture 01
Tue, Jan 20, 2009 1800 : 2100
FAST NU, Karachi
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
2/21
2
Course Outline Introduction to Data Warehousing and Background
Dimension Modeling
Architecture and Infrastructure
Extract Transform Load
Data Quality Management
OLAP
Implementation Methods of Data Warehouse
Data Mining Overview
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
3/21
3
Course Material Data Warehousing Fundamentals
by Paulraj Ponniah
John Wiley and SonsArticles
Class Notes
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
4/21
Marks Distribution
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
5/21
Objective of the course Why exactly the world needs a Data Warehouse?
How Data Warehouse differs from traditional databasesand RDBMS?
Where does OLAP stands in the Data Warehouse picture?
What are different Data Warehouse and OLAPmodels/schemas?
How to perform ETL? What is data cleansing? How toperform it? What are the famous algorithms?
Which different Data Warehouse architectures are there?What are their strengths and weaknesses?
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
6/21
6
What is a Data Warehouse? The Data Warehouse is an integrated, subject-
oriented, time-variant, non-volatile database thatprovides support for decision making
Decision Support is a methodology (or a series ofmethodologies) designed to extract information from data andto use such information as a basis for decision making
Subject Oriented
Organized along thelines of the subjects ofthe corporation. Typicalsubjects are customer,product, vendor and
transaction.
Time Variant
Every record in the datawarehouse has someform of time dimensionattached to it.
Non Volatile
Refers to the inability ofdata to be updated. Everyrecord in the datawarehouse is timestamped in one form or
the other.
Integrated
Single, Enterprise-Wideview.
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
7/217
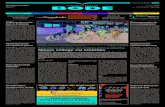
What is a Data Warehouse?
LegacyData
Corporate Decision Support Infrastructure
DWReporting
ServersEndUser
Large ScaleData
Collection
Generation orDigitization
Exercise
OnlineOperational
Source
OnlineOperational
Source
Online
OperationalSource
OnlineOperational
Source
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
8/218
Needs for Strategic Information Retain the present customer base
Increase the customer base by 15% over the next 5
years Gain market share by 10% in the next 3 years
Improve product quality levels in the top five productgroups
Enhance customer service level in shipments Bring three new products to market in 2 years
Increase sales by 15% in the Northern Division
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
9/219
Need of a Data Warehouse The amount of data the average business collects and
stores is doubling each year Total hardware and software cost to store and manage
1 Mbyte of data 1990: ~ $15 2002: ~ 15 (Down 100 times) 2005: ~ 1 (Down 1500 times)
A Few Examples Cern: Up to 20 PB by 2006 Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC): 500TB France Telecom: ~ 100 TB WalMart: 24 TB
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
10/2110
Operational Systems User needs information
User requests reports from IT
IT places request on backlog IT creates ad queries
IT sends requested reports
User hopes to find the right answer
User needs information
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
11/2111
Operational vs. InformationalOperational InformationalData Content Current values Archived, derived,
summarized
Data StructureOptimized for transactions Optimized for complex
queries
Access
Frequency
High Medium to low
Access Type Read, update, delete Read
Usage Predictable, repetitive Ad hoc, random, heuristic
Response Time Sub seconds Several seconds to minutes
Users Large number Relatively small number
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
12/21
12
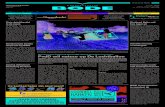
Data WarehouseInformation Sources Data Warehouse
Server
(Tier 1)
OLAP Servers
(Tier 2)
Clients
(Tier 3)
Operational
DBs
Semistructured
Sources
extract
transform
load
refresh
etc.
Data Marts
Data
Warehouse
e.g., MOLAP
e.g., ROLAP
serve
Analysis
Query/Reporting
Data Mining
serve
serve
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
13/21
13
Online Transaction Processing
(OLTP)Also known as operational sources Day-to-day handling of transactions that result from
enterprise operation
Airline reservation systems, Electronic point of salesystems, Automatic teller machines etc Typically several systems within same enterprise Read and Update mostly
Standard, Predefined, less complex queries Queries based on individual or a relatively less number
of records (Single-Hit Queries) Typically used in Tactical Management
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
14/21
14
Decision Support Systems Decision Support is a methodology (or a series of
methodologies) designed to extract information fromdata and to use such information as a basis for decisionmaking
Communication Driven DSS
Data Driven DSS
Document Driven DSS Knowledge Driven DSS
Model Driven DSS
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
15/21
15
Data Driven DSS
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
16/21
16
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Goal of OLAP is to support ad-hoc querying for the
business analyst
Multidimensional view of data is the foundation of
OLAP Extend spreadsheet analysis model to work with
warehouse data Read Only Access
Semantically enriched to understand business terms(e.g., time, geography)
Combined with reporting features
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
17/21
17
OLTP vs. Data Driven DSSTrait OLTP Data Driven DSS
User Sales Staff, IT Professionals Knowledge worker
Function Day to day operations Decision support
DB Design Application-oriented (E-R based) Subject-oriented (Star, snowflake)
Data Current, Isolated Historical, Consolidated
View Detailed, Flat relational Summarized, Multidimensional
Usage Structured, Repetitive Ad hoc
Unit of work Short, Simple transaction Complex query
Access Read/write Read Mostly
Operations Index/hash on primary key Lots of Scans
Records accessed Tens to Hundreds Thousands to Millions
#Users Thousands Hundreds
Db size 100 MB-GB 100GB-TB
Metric Trans. throughput Query throughput, response
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
18/21
18
Data Mining Knowledge Extraction
Verification: OLAP type analyses, hypothesis testing
Discovery: Extracting rules or patterns
Data Mining is finding hidden patterns in data Predict which customers will buy new policies
Identify behavior patterns of risky customers
Identify fraudulent behavior Characterize patient behavior to predict office visits
Identify successful medical therapies for different illnesses
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
19/21
19
Knowledge Discovery in Databases
(KDD) Non-trivial extraction of implicit, previously unknown
and potentially useful knowledge from data
KDD stages Problem definition
Data selection
Cleaning
Enrichment Coding and organization
Data mining
Reporting
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
20/21
20
DW and DB
Clarifying Confusions Is DW different from DB
No
The difference is historical not technical DW is a DB inside and out
DW is to Data Driven DSS what DB is to OLTP
-
7/29/2019 DW Lecture 01
21/21
21
Brief History of DB Design Master file design
Integrated, subject-oriented design
Relational design Star join design