DW Concept
-
Upload
harry-anderson -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of DW Concept
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
1/27
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
2/27
Information System
The aim of information system is to support operations and
decision making.
Types of Information system: Online transaction processing(OLTP)
Data Warehouse(DW)
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
3/27
Online transaction processing System
OLTP contains commercial transaction or operational data.
It is a up to date system.
Database updates whenever a new transaction is performed.
OLTP system stores data of few weeks or months.
OLTP have normalized schema to optimize the DML
statement.
Example: Credit card transaction, Reservation system, booking
system, billing system, accounting system, banking system
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
4/27
Data Warehouse System
The Data warehouse is :
Subject oriented
Integrated
Time variant
Non volatile
Collection of data which is used for decision making purpose.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
5/27
Data Warehouse System(Contd.)
DW system contains historical data.
It is not a up to date system.
Database updates on daily or weekly basis.
DW system stores many years of data.
DW have Denormalized schema.
It is used for reporting purpose.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
6/27
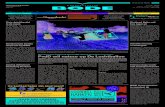
DW Architecture (ETL with stage area)
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
7/27
Why Staging area is required
Single platform for all sources.
Optimize performance of ETL.
Do not hamper the performance of OLTP system.
Easily restart load after failure.
Simplified the job of testing in case of XML or Cobol source
data
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
8/27
ODS layer
ODS layer presents between the OLTP and DW system.
ODS is a replica of your OLTP systems.
suppose you want to analyze live data or current data then we
use ODS layer.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
9/27
Dimensional modeling
In DW we use Dimensional modeling but in OLTP we use ER
modeling.
Terms used in dimension modeling are-
Dimension
Attribute
Fact
Types of Schema to represent a dimensional model
Star Schema
Snowflake Schema
Fact Constellation
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
10/27
Dimension
Dimension is used to categorize the data.
Dimension has attributes.
All dimension has one primary key.
Example for sales data warehouse dimension would beproduct, customer, time and store.
Product
Product_ID
NameExpiry _date
Mfr_date
Manufacturer
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
11/27
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
12/27
Conformed Dimension
A dimension having same structure in all data marts.
Create it only once and refer it in all data marts.
Example: Product dimension is used in sales and inventory
data mart. It has same structure in both data marts.
Product
Product_id
Product_name
Mfg_date
Expiry_date
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
13/27
Slowly Changing Dimension
In SCD attributes are changed with time .
Example in customer dimension address, email id and contact
no can be changed with time.
Types of Dimension
SCD I
SCD II
SCD III
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
14/27
Slowly Changing Dimension I
Always Update records if already present.
History is not maintained.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
15/27
Slowly Changing Dimension II
Create a new row for each record. No updation only insertion.
History is maintained.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
16/27
Slowly Changing Dimension III
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
17/27
Fact table
Fact tables contains measures and numerical data.
It represent a value with respect to a combination of all
dimension.
A fact table has foreign key for all dimensions.
A fact table has a primary key to represent unique transaction.
Example sales table
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
18/27
Fact table(Contd.)
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
19/27
Factless fact table
A factless fact table doesnt contain any measures.
For example Student attendance
Fact_Attendance
Student_id
Class_id
Time_id
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
20/27
Junk Dimension
Junk dimension is a group of low cardinality attributes.
Example Voucher_ind and payback_ind
Sales fact table
Product_id
Customer_id
Txn_id
Store_id
Voucher_indPayback_ind
Txn_AMT
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
21/27
Junk Dimension(Contd.)
There are two ways to handle low cardinality attributes.
First way is two create two dimension for each of attribute.
Second way: use junk dimension.
First way is not a good practice because if no of indicators
Increases the no of dimension tables will also increase.
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
22/27
Junk Dimension(Contd.)
Junk_id Voucher_id Payback_Ind
1 Y N
2 N Y
3 N N
4 Y Y
Sales fact table
Product_id
Customer_id
Txn_id
Store_id
Junk_id
Txn_AMT
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
23/27
Degenerate Dimension
The items in fact table which is neither measure nor related to
dimension is consider as Degenerate dimension
Degenerate dimension always has one attribute. Rater than
creating a separate dimension we merge this in fact table.
Degenerate dimension is a unique no which generate at time
of transaction.
Bill no can be a degenerate dimension.
Sales fact tableBill no
Prod_id
Cust_id
Time_id
Price_amount
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
24/27
Star Schema
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
25/27
Snowflake Schema
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
26/27
Fact Constellation or Galaxy Schema
-
7/27/2019 DW Concept
27/27
Thanks