Bone Tumor Gopal
-
Upload
jennifer-dixon -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
0
Transcript of Bone Tumor Gopal
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
1/53
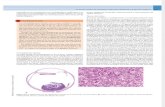
OSTEOSARCOMA
Gopal Singh
Lecturer
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
2/53
Oncology defined
Branch of medicine that deals with the
study, detection, treatment and
management of cancer and neoplasia
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
3/53
Root words
Neo- new
Plasia- growth
Plasm- substance
Trophy- size
+Oma- tumor
Statis- location
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
4/53
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
5/53
Characteristics of Neoplasia
Uncontrolled growth of Abnormal cells
1. Benign
2. Malignant
3. Borderline
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
6/53
Characteristics of Neoplasia
Benign
Well-differentiated
Slow growth
Encapsulated
Non-invasive
Does NOT metastasize
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
7/53
Characteristics of Neoplasia
Malignant
Undifferentiated
Erratic and Uncontrolled Growth
Expansive and Invasive
Secretes abnormal proteins
Metastasizes
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
8/53
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
9/53
Age(probably the most important clinical clue).
Age groupMost common b enign
les ions
Most common m alignant
tumors
0 - 10simple bone cyst
eosinophilic granuloma
Ewing's sarcoma
leukemic involvementmetastatic neuroblastoma
10 - 20
non-ossifying fibroma
fibrous dysplasia
simple bone cyst
aneurysmal bone cyst
osteochondroma (exostosis)osteoid osteoma
osteoblastoma
chondroblastoma
chondromyxoid fibroma
osteosarcoma,
Ewing's sarcoma,adamantinoma
20 - 40enchondroma
giant cell tumorchondrosarcoma
40 & above osteoma
metastatic tumorsmyeloma
leukemic involvement
chondrosarcoma
osteosarcoma (Paget's
associated)
MFH
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
10/53
Defination
Osteosarcoma is the name given to aheterogeneous group of malignant spindle celltumors that have as their common feature the
production of immature bone, also known asOSTEOID.
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
11/53
Epidemiology
It is the second most common primary
malignancy of bone
The incidence is approximately 1-3 per 1
million per year.
Male>female
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
12/53
Epidemiology
Most common sites are the
Distal femur
Proximal tibia Proximal humerus
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
13/53
Risk Factors/Etiology
The exact cause of osteosarcoma is
unknown
Rapid bone growth
Environmental factors (exposure to radiation
)
Known causative agents are divided into
Chemicals
Viruses
radiation
miscellaneous
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
14/53
Classification
Osteosarcomas are categorized asprimary or secondary.
Primary Osteosarcomas are
Conventional osteosarcoma, Low-grade intramedullary osteosarcoma,
Parosteal osteosarcoma,
Periosteal osteosarcoma,
High-grade surface osteosarcoma, Telangiectatic osteosarcoma, and
Small cell osteosarcoma
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
15/53
Classification .
Secondary osteosarcomas
Osteosarcomas occurring at the site of
another disease process The most common are
Paget disease
Previous radiation treatment
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
16/53
Classification .
Other associated conditions are Fibrous dysplasia,
Bone infarcts,
Osteochondromas, Chronic osteomyelitis,
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
17/53
Clinical feature
Pain
The pain may be progressive for manymonths, and initially be confused with
more common sources such as musclesoreness, overuse injury or "growingpains."
Night pain is an important clue to the truediagnosis (25%)
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
18/53
Clinical feature
Swelling
Palpable mass is noted in up to 1/3 ofpatients at the first visit
LimpIn smaller children, a limp may be the onlysymptom
Restriction of movement of the adjacent
joint Pathological Fracture
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
19/53
Lab: Investigation
Full blood count, ESR, CRP.
LDHALP (elevated levels at diagnosis signify
increased risk of pulmonary metastasis) Platelet count
Electrolyte levels Liver function tests Renal function tests
Urinalysis
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
20/53
Radiology: Investigation
CT scanning
CT scanning of the chest is more sensitive than is plainfilm radiography for assessing pulmonary metastases.
MRIMRI of the primary lesion is the best method to assessthe extent of intramedullary disease as well asassociated soft-tissue masses and skip lesions.
Bone ScanA bone scan should be obtained to look for skeletal
metastases or multi focal disease.
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
21/53
Others Investigation
Thallium scanMonitor effects of chemotherapyDetect local recurrence of tumor
AngiographyDetect vascular displacement anddetermine relationship of vessels to the
tumorIdentify vascular anomalies
Estimate effects of chemotherapy.
Once all the initial imaging & lab exam hasbeen done biopsy is performed to con formthe diagnosis.
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
22/53
Biopsy
Biopsy
Principles of Biopsy:
A biopsy should be planned as carefully
as the definitive procedure.
Biopsy should be done only after complete
clinical, laboratory, and radiographicexaminations.
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
23/53
Biopsy
Transverse incisions should be avoided.
The deep incision should go through asingle muscle compartment.
Biopsy should be taken from the peripheryof a lesion as it usually contains the most
viable tissue.
The wound should be closed tightly inlayers.
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
24/53
Types of biopsy
Fine needle aspiration
Core needle biopsy
Open incisional biopsy
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
25/53
Staging
The staging system devised and
introduced by Enneking in 1980 is applies
to all musculoskeletal tumors.
Staging system are the
Histologic grade of the tumor
(low grade vs high grade)
Anatomic location of the tumor intracompartmental vs extracompartmental
Absence or presence of metastatic disease
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
26/53
Staging ..
Stage I: Low grade tumors
I-A intra compartmental
I-B extra compartmental
Stage II: High grade tumors
II-A intra compartmental
II-B extra compartmental
Stage III: Any tumors with evidence ofmetastasis
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
27/53
Staging
American Joint Committee on Cancer Systemfor Staging Bone Sarcomas
Based on grade & size of tumor and presence
of metastasisStage Grade Size MetastasesI-A Low 8 cm NoneI-B Low >8 cm None
II-A High 8 cm NoneII-B High >8 cm NoneIII Any Any Skip metastasisIV-A Any Any Pulmonary metastasesIV-B Any Any Nonpulmonary metastases
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
28/53
Treatment
1. Radiological staging
2. Biopsy to confirm diagnosis
3. Preoperative chemotherapy
4. Repeat radiological staging(access chemo response, finalize surgical tx plan)
5. Surgical resection with wide margin
6. Reconstruction using one of many
techniques
7. Post op chemo based on preop response
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
29/53
Treatment .
The drugs used most often to treatosteosarcoma are: Methotrexate with leucovorin (folinic acid)
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Cisplatin or carboplatin
Etoposide
Ifosfamide
CyclophosphamideActinomycin D (dactinomycin)
Bleomycin
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
30/53
Treatment ..
Some common combinations of drugsinclude:
Cisplatin and Adriamycin (CA)
Vincristine, Methotrexate, Leucovorin &
Adriamycin
High-dose methotrexate, Adriamycin, and
cisplatin (sometimes with ifosfamide) Dactinomycin, bleomycin and cyclophosphamide
Ifosfamide and Etoposide
frequency....... Repeat cycle every 21 days
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
31/53
Side effect
General side effects: Nausea and vomiting, Loss of appetite, Hair loss,
Mouth sores.
Chemotherapy can damage the blood-producing cells resulting in:
Increased chance of infection ( W B C) Bleeding or bruising (Platelets) Fatigue or shortness of breath (RBCs)
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
32/53
Side effect..
Side effects of specific drugs. Ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide : hemorrhagic cystitis.
Cisplatin: neuropathy, nephropathy, ototoxicity.
High-dose methotrexate: leukoencephalopathy and liver or kidney
damage. Doxorubicin (Adriamycin): can cause heart damage over time.
Long-term side effects:
Infertility
Heart damage
Developing a second cancer(
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
33/53
Surgery
The main goal of surgery is to safely andcompletely remove the tumor.
Historically, most patients had an amputation.
Wide resection & prosthetic knee replacement Transfemoral amputation is common
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
34/53
Complication of surgery
Hematoma
Infection
Wound necrosis
Contracture Pain
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
35/53
Ewings Sarcoma
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
36/53
Introduction
Identified in 1921 by James Ewing
Differed from osteogenic sarcoma
Different location
Poor survival: 5-10% at 5 years
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
37/53
Epidemiology
Incidence is 0.6 per million
Males > Females
Rare in blacks and Asians
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
38/53
Clinical Features
Pain most commonly (90%)
Swelling (70%)
Fever (20%)
Pathological fracture
Weight loss
Malaise
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
39/53
Clinical Features ..
Local warmth, inflammation
Pleural effusions
Neurological signs if spinal involvement
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
40/53
Investigation
ESR
LDH
Anemia
Leukocytosis
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
41/53
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
42/53
Investigation: Radiology
Site
Size
Effect on bone
Response of Bone
Matrix
Cortex
Soft tissue
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
43/53
Staging
Local and distal staging
Bone marrow aspirate
Pre-chemotherapy investigations
Biopsy
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
44/53
Staging
Location
Tumor Size
Metastases at diagnosis
Response to chemotherapy
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
45/53
Treatment
Multidisciplinary approach
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Surgery
Radiation
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
46/53
Nursing Intervention
Promote Nutrition
Serve food in ways to make it appealing
Provide small frequent meals
Avoids giving fluids while eating
Oral hygiene PRIOR to mealtime
Vitamin supplements
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
47/53
Nursing Intervention..
Relieve Pain
Mild pain- NSAIDS
Moderate pain- Weak opiods
Severe pain- Morphine
Administer analgesics round the clock with
additional dose for breakthrough pain
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
48/53
Nursing Intervention..
Decrease Fatigue
Plan daily activities to allow alternating rest
periods
Light exercise is encouraged
Small frequent meals
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
49/53
Nursing Intervention..
Improve body image
Therapeutic communication is essential
Encourage independence in self-care and
decision making
Offer cosmetic material like make-up and wigs
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
50/53
Nursing Intervention..
Assist in the grieving process
Some cancers are curable
Grieving can be due to loss of health, income,
sexuality, and body image
Answer and clarify information about cancer
and treatment options
Identify resource people Refer to support groups
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
51/53
Nursing Intervention..
Manage Complication: Infection
Fever is the most important sign (38.3)
Administer prescribed antibiotics X
2weeks Maintain aseptic technique
Avoid exposure to crowds
Avoid giving fresh fruits and veggie Handwashing
Avoid frequent invasive procedures
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
52/53
Nursing Intervention..
Manage complication: septic shock
Monitor VS, BP, temp
Administer IV antibiotics
Administer supplemental O2
-
8/11/2019 Bone Tumor Gopal
53/53
Nursing Intervention..
Manage Complication: Bleeding
Thrombocytopenia (